This is an old revision of the document!
Table of Contents
Formatting Syntax
The Picnic Time knowledge base supports some simple markup language, which tries to make the datafiles to be as readable as possible. This page contains all possible syntax you may use when editing the pages. Simply have a look at the source of this page by pressing “Edit this page” or “Show pagesource”. The simpler markup is easily accessible via quick buttons, too.
Basic Text Formatting
The knowledge base supports bold, italic, underlined and monospaced texts. Of course you can combine all these.
the knowledge base supports **bold**, //italic//, __underlined__ and ''monospaced'' texts. Of course you can **__//''combine''//__** all these.
You can use subscript and superscript, too.
You can use <sub>subscript</sub> and <sup>superscript</sup>, too.
You can mark something as deleted as well.
You can mark something as <del>deleted</del> as well.
Paragraphs are created from blank lines. If you want to force a newline without a paragraph, you can use two backslashes followed by a whitespace or the end of line.
This is some text with some linebreaks
Note that the
two backslashes are only recognized at the end of a line
or followed by
a whitespace \\this happens without it.
This is some text with some linebreaks\\ Note that the two backslashes are only recognized at the end of a line\\ or followed by\\ a whitespace \\this happens without it.
You should use forced newlines only if really needed.
Links
The knowledge base supports multiple ways of creating links.
External
External links are recognized automagically: http://www.google.com or simply www.google.com - You can set the link text as well: This Link points to google. Email addresses like this one: andre@picnictime.com are recognized, too.
The knowledge base supports multiple ways of creating links. External links are recognized automagically: http://www.google.com or simply www.google.com - You can set link text as well: [[http://www.google.com|This Link points to google]]. Email addresses like this one: <andre@picnictime.com> are recognized, too.
Internal
Internal links are created by using square brackets. You can either just give a pagename or use an additional link text.
Internal links are created by using square brackets. You can either just give a [[pagename]] or use an additional [[pagename|link text]].
Knowledge base pagenames are converted to lowercase automatically, special characters are not allowed.
You can use namespaces by using a colon in the pagename.
You can use [[some:namespaces]] by using a colon in the pagename.
Linking to a specific section is possible, too. Just add the section name behind a hash character as known from HTML. This links to this Section.
This links to [[syntax#internal|this Section]].
Notes:
- Links to existing pages are shown in a different style from nonexisting ones.
- The knowledge base does not use CamelCase to automatically create links by default, but this behavior can be enabled in the config file.
- When a section's heading is changed, its bookmark changes, too. So don't rely on section linking too much.
Windows Shares
Windows shares like this are recognized, too. Please note that these only make sense within our office network and are now usually blocked by web browsers.
Windows Shares like [[\\PTFILES\CompanyShared|this]] are recognized, too.
Image Links
You can also use an image to link to another internal or external page by combining the syntax for links and images (see below) like this:
[[http://www.picnictime.com|{{wiki:ptlogo.png}}]]
Please note: The image formatting is the only formatting syntax accepted in link names.
The whole image and link syntax is supported (including image resizing, internal and external images and URLs and interwiki links).
Footnotes
You can add footnotes 1) by using double parentheses.
You can add footnotes ((This is a footnote)) by using double parentheses.
Sectioning
You can use up to five different levels of headlines to structure your content. If you have more than three headlines, a table of contents is generated automatically – this can be disabled by including the string ~~NOTOC~~ in the document.
Headline Level 3
Headline Level 4
Headline Level 5
==== Headline Level 3 ==== === Headline Level 4 === == Headline Level 5 ==
By using four or more dashes, you can make a horizontal line:
Media Files
You can include external and internal images, videos and audio files with curly brackets. Optionally you can specify the size of them.
Resize to given width and height2): 
Real size: {{wiki:ptlogo.png}}
Resize to given width: {{wiki:ptlogo.png?50}}
Resize to given width and height: {{wiki:ptlogo.png?200x50}}
Resized external image: {{https://www.google.com/images/branding/googlelogo/1x/googlelogo_color_272x92dp.png?200x50}}
By using left or right whitespaces you can choose the alignment.
{{ wiki:ptlogo.png}}
{{wiki:ptlogo.png }}
{{ wiki:ptlogo.png }}
Of course, you can add a title (displayed as a tooltip by most browsers), too.
{{ wiki:ptlogo.png |This is the caption}}
For linking an image to another page see Image Links above.
Supported Media Formats
The knowledge base can embed the following media formats directly.
| Image | gif, jpg, png |
| Video | webm, ogv, mp4 |
| Audio | ogg, mp3, wav |
| Flash | swf |
If you specify a filename that is not a supported media format, then it will be displayed as a link instead.
By adding ?linkonly you provide a link to the media without displaying it inline
{{wiki:ptlogo.png?linkonly}}
ptlogo.png This is just a link to the image.
Fallback Formats
Unfortunately not all browsers understand all video and audio formats. To mitigate the problem, you can upload your file in different formats for maximum browser compatibility.
For example consider this embedded mp4 video:
{{video.mp4|A funny video}}
When you upload a video.webm and video.ogv next to the referenced video.mp4, the knowledge base will automatically add them as alternatives so that one of the three files is understood by your browser.
Additionally the knowledge base supports a “poster” image which will be shown before the video has started. That image needs to have the same filename as the video and be either a jpg or png file. In the example above a video.jpg file would work.
Lists
The knowledge base supports ordered and unordered lists. To create a list item, indent your text by two spaces and use a * for unordered lists or a - for ordered ones.
- This is a list
- The second item
- You may have different levels
- Another item
- The same list but ordered
- Another item
- Just use indention for deeper levels
- That's it
* This is a list
* The second item
* You may have different levels
* Another item
- The same list but ordered
- Another item
- Just use indention for deeper levels
- That's it
Text Conversions
The knowledge base can convert certain pre-defined characters or strings into images or other text or HTML.
The text to image conversion is mainly done for smileys. And the text to HTML conversion is used for typography replacements, but can be configured to use other HTML as well.
Text to Image Conversions
The knowledge base converts commonly used emoticons to their graphical equivalents. Those Smileys and other images can be configured and extended. Here is an overview of Smileys included in the knowledge base:
 8-)
8-)  8-O
8-O  :-(
:-(  :-)
:-)  =)
=)  :-/
:-/  :-\
:-\  :-?
:-?  :-D
:-D  :-P
:-P  :-O
:-O  :-X
:-X  :-|
:-|  ;-)
;-)  ^_^
^_^  :?:
:?:  :!:
:!:  LOL
LOL  FIXME
FIXME  DELETEME
DELETEME
Text to HTML Conversions
Typography: the knowledge base can convert simple text characters to their typographically correct entities. Here is an example of recognized characters.
→ ← ↔ ⇒ ⇐ ⇔ » « – — 640×480 © ™ ® “He thought 'It's a man's world'…”
-> <- <-> => <= <=> >> << -- --- 640x480 (c) (tm) (r) "He thought 'It's a man's world'..."
The same can be done to produce any kind of HTML, it just needs to be added to the pattern file.
There are three exceptions which do not come from that pattern file: multiplication entity (640×480), 'single' and “double quotes”. They can be turned off through a config option.
Quoting
Some times you want to mark some text to show it's a reply or comment. You can use the following syntax:
I think we should do it > No we shouldn't >> Well, I say we should > Really? >> Yes! >>> Then lets do it!
I think we should do it
No we shouldn't
Well, I say we should
Really?
Yes!
Then lets do it!
Tables
The knowledge base supports a simple syntax to create tables.
| Heading 1 | Heading 2 | Heading 3 |
|---|---|---|
| Row 1 Col 1 | Row 1 Col 2 | Row 1 Col 3 |
| Row 2 Col 1 | some colspan (note the double pipe) | |
| Row 3 Col 1 | Row 3 Col 2 | Row 3 Col 3 |
Table rows have to start and end with a | for normal rows or a ^ for headers.
^ Heading 1 ^ Heading 2 ^ Heading 3 ^ | Row 1 Col 1 | Row 1 Col 2 | Row 1 Col 3 | | Row 2 Col 1 | some colspan (note the double pipe) || | Row 3 Col 1 | Row 3 Col 2 | Row 3 Col 3 |
To connect cells horizontally, just make the next cell completely empty as shown above. Be sure to have always the same amount of cell separators!
Vertical tableheaders are possible, too.
| Heading 1 | Heading 2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Heading 3 | Row 1 Col 2 | Row 1 Col 3 |
| Heading 4 | no colspan this time | |
| Heading 5 | Row 2 Col 2 | Row 2 Col 3 |
As you can see, it's the cell separator before a cell which decides about the formatting:
| ^ Heading 1 ^ Heading 2 ^ ^ Heading 3 | Row 1 Col 2 | Row 1 Col 3 | ^ Heading 4 | no colspan this time | | ^ Heading 5 | Row 2 Col 2 | Row 2 Col 3 |
You can have rowspans (vertically connected cells) by adding ::: into the cells below the one to which they should connect.
| Heading 1 | Heading 2 | Heading 3 |
|---|---|---|
| Row 1 Col 1 | this cell spans vertically | Row 1 Col 3 |
| Row 2 Col 1 | Row 2 Col 3 | |
| Row 3 Col 1 | Row 2 Col 3 |
Apart from the rowspan syntax those cells should not contain anything else.
^ Heading 1 ^ Heading 2 ^ Heading 3 ^ | Row 1 Col 1 | this cell spans vertically | Row 1 Col 3 | | Row 2 Col 1 | ::: | Row 2 Col 3 | | Row 3 Col 1 | ::: | Row 2 Col 3 |
You can align the table contents, too. Just add at least two whitespaces at the opposite end of your text: Add two spaces on the left to align right, two spaces on the right to align left and two spaces at least at both ends for centered text.
| Table with alignment | ||
|---|---|---|
| right | center | left |
| left | right | center |
| xxxxxxxxxxxx | xxxxxxxxxxxx | xxxxxxxxxxxx |
This is how it looks in the source:
^ Table with alignment ^^^ | right| center |left | |left | right| center | | xxxxxxxxxxxx | xxxxxxxxxxxx | xxxxxxxxxxxx |
Note: Vertical alignment is not supported.
No Formatting
If you need to display text exactly like it is typed (without any formatting), enclose the area either with <nowiki> tags or even simpler, with double percent signs %%.
This is some text which contains addresses like this: http://www.picnictime.com and **formatting**, but nothing is done with it. The same is true for //__this__ text// with a smiley ;-).
<nowiki> This is some text which contains addresses like this: http://www.picnictime.com and **formatting**, but nothing is done with it. </nowiki> The same is true for %%//__this__ text// with a smiley ;-)%%.
Code Blocks
You can include code blocks into your documents by either indenting them by at least two spaces (like used for the previous examples) or by using the tags <code> or <file>.
This is text is indented by two spaces.
This is preformatted code all spaces are preserved: like <-this
This is pretty much the same, but you could use it to show that you quoted a file.
Those blocks were created by this source:
This is text is indented by two spaces.
<code> This is preformatted code all spaces are preserved: like <-this </code>
<file> This is pretty much the same, but you could use it to show that you quoted a file. </file>
Syntax Highlighting
The knowledge base can highlight sourcecode, which makes it easier to read. It uses the GeSHi Generic Syntax Highlighter – so any language supported by GeSHi is supported. The syntax uses the same code and file blocks described in the previous section, but this time the name of the language syntax to be highlighted is included inside the tag, e.g. <code java> or <file java>.
/** * The HelloWorldApp class implements an application that * simply displays "Hello World!" to the standard output. */ class HelloWorldApp { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("Hello World!"); //Display the string. } }
The following language strings are currently recognized: 4cs, 6502acme, 6502kickass, 6502tasm, 68000devpac, abap, actionscript-french, actionscript, actionscript3, ada, algol68, apache, applescript, asm, asp, autoconf, autohotkey, autoit, avisynth, awk, bascomavr, bash, basic4gl, bf, bibtex, blitzbasic, bnf, boo, c, c_loadrunner, c_mac, caddcl, cadlisp, cfdg, cfm, chaiscript, cil, clojure, cmake, cobol, coffeescript, cpp, cpp-qt, csharp, css, cuesheet, d, dcs, delphi, diff, div, dos, dot, e, epc, ecmascript, eiffel, email, erlang, euphoria, f1, falcon, fo, fortran, freebasic, fsharp, gambas, genero, genie, gdb, glsl, gml, gnuplot, go, groovy, gettext, gwbasic, haskell, hicest, hq9plus, html, html5, icon, idl, ini, inno, intercal, io, j, java5, java, javascript, jquery, kixtart, klonec, klonecpp, latex, lb, lisp, llvm, locobasic, logtalk, lolcode, lotusformulas, lotusscript, lscript, lsl2, lua, m68k, magiksf, make, mapbasic, matlab, mirc, modula2, modula3, mmix, mpasm, mxml, mysql, newlisp, nsis, oberon2, objc, objeck, ocaml-brief, ocaml, oobas, oracle8, oracle11, oxygene, oz, pascal, pcre, perl, perl6, per, pf, php-brief, php, pike, pic16, pixelbender, pli, plsql, postgresql, povray, powerbuilder, powershell, proftpd, progress, prolog, properties, providex, purebasic, pycon, python, q, qbasic, rails, rebol, reg, robots, rpmspec, rsplus, ruby, sas, scala, scheme, scilab, sdlbasic, smalltalk, smarty, sql, systemverilog, tcl, teraterm, text, thinbasic, tsql, typoscript, unicon, uscript, vala, vbnet, vb, verilog, vhdl, vim, visualfoxpro, visualprolog, whitespace, winbatch, whois, xbasic, xml, xorg_conf, xpp, yaml, z80, zxbasic
Downloadable Code Blocks
When you use the <code> or <file> syntax as above, you might want to make the shown code available for download as well. You can do this by specifying a file name after language code like this:
<file php myexample.php> <?php echo "hello world!"; ?> </file>
- myexample.php
<?php echo "hello world!"; ?>
If you don't want any highlighting but want a downloadable file, specify a dash (-) as the language code: <code - myfile.foo>.
Embedding HTML and PHP
You can embed raw HTML or PHP code into your documents by using the <html> or <php> tags. (Use uppercase tags if you need to enclose block level elements.)
HTML example:
<html> This is some <span style="color:red;font-size:150%;">inline HTML</span> </html> <HTML> <p style="border:2px dashed red;">And this is some block HTML</p> </HTML>
This is some inline HTML
And this is some block HTML
PHP example:
<php> echo 'The PHP version: '; echo phpversion(); echo ' (generated inline HTML)'; </php> <PHP> echo '<table class="inline"><tr><td>The same, but inside a block level element:</td>'; echo '<td>'.phpversion().'</td>'; echo '</tr></table>'; </PHP>
The PHP version: 5.5.30 (inline HTML)
| The same, but inside a block level element: | 5.5.30 |
Please Note: HTML and PHP embedding is disabled by default in the configuration. If disabled, the code is displayed instead of executed.
RSS/ATOM Feed Aggregation
The knowledge base can integrate data from external XML feeds.You can influence the rendering by multiple additional space separated parameters:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| any number | will be used as maximum number items to show, defaults to 8 |
| reverse | display the last items in the feed first |
| author | show item authors names |
| date | show item dates |
| description | show the item description. If HTML is disabled all tags will be stripped |
| nosort | do not sort the items in the feed |
| n[dhm] | refresh period, where d=days, h=hours, m=minutes. (e.g. 12h = 12 hours). |
The refresh period defaults to 4 hours. Any value below 10 minutes will be treated as 10 minutes. The knowledge base will generally try to supply a cached version of a page, obviously this is inappropriate when the page contains dynamic external content. The parameter tells the knowledge base to re-render the page if it is more than refresh period since the page was last rendered.
By default the feed will be sorted by date, newest items first. You can sort it by oldest first using the reverse parameter, or display the feed as is with nosort.
Example:
{{rss>http://slashdot.org/index.rss 5 author date 1h }}
- Illinois Health Department Exposed Over 700,000 Residents' Personal Data For Years by BeauHD (2026/01/08 16:50)
- Google Is Adding an 'AI Inbox' To Gmail That Summarizes Emails by BeauHD (2026/01/08 16:10)
- French Court Orders Google DNS to Block Pirate Sites, Dismisses 'Cloudflare-First' Defense by BeauHD (2026/01/08 15:30)
- Microsoft Turns Copilot Chats Into a Checkout Lane by BeauHD (2026/01/08 14:50)
- Wi-Fi Advocates Get Win From FCC With Vote To Allow Higher-Power Devices by BeauHD (2026/01/08 14:10)
Control Macros
Some syntax influences how DokuWiki renders a page without creating any output it self. The following control macros are availble:
| Macro | Description |
|---|---|
| ~~NOTOC~~ | If this macro is found on the page, no table of contents will be created |
| ~~NOCACHE~~ | The knowledge base caches all output by default. Sometimes this might not be wanted (eg. when the <php> syntax above is used), adding this macro will force the knowledge base to rerender a page on every call |
Diagrams
Basics
Diagrams must be used within a special tag. It's because their syntax is similar to table syntax. To insert diagram into a code you should write the following:
<diagram> Diagram specification </diagram>
Diagram specification is a multiline expression. Each line consists of control characters, that define links between blocks, and letter sequences, that define blocks. These entities are separated by the special character `|'. For example, the following specification
<diagram> | AAA |-| BBB | | |:| | | | | | | |L|~|~| CCC | </diagram>
defines this diagram:
| AAA | BBB | |||||||||||||
| CCC | ||||||||||||||
You can write any text instead of letter sequences for block description except the case of special characters.
<diagram> | root |-| 1-st branch | | |:| | | | | | | |L|~|~| 2-nd branch | </diagram>
| root | 1-st branch | |||||||||||||
| 2-nd branch | ||||||||||||||
Unfortunately, this method breaks down text representation of diagram (for large diagram this leads to difficulty in changing wiki-code) and also doesn't allow to use wiki-syntax within a block. To overcome this you should consider sequences of letters, digits and underscore as abbreviations and decode them at the end of a line using the equal sign and `|' symbol as a separator. For example:
<diagram> | AAA |-| BBB |AAA=root|BBB=1<sup>st</sup> branch (see [[wp>Branch]]) | |:| | | | | | | |L|~|~| CCC |CCC=2<sup>nd</sup> branch\\ **(very important branch)** </diagram>
| root | 1st branch (see Branch) | |||||||||||||
| 2nd branch (very important branch) |
||||||||||||||
You can describe family trees using such diagrams.
<diagram> | | | Dad |y| Mom | | |Dad=Daddy|Mom=Mommy | |,|-|-|-|+|-|-|-|.| | | Sys | | Me | | Bro |Sys=Syster|Bro=Brother </diagram>
| Daddy | Mommy | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Syster | Me | Brother | ||||||||||||||||||||
All types of connections are shown in the following table:
| , | . | ` | ' | ^ | v | ( | ) | - | ! | + |
 |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| F | 7 | L | J | A | V | C | D | ~ | : | % |
 |  |  |  | 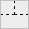 |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| y | h | } | { | p | b | ] | [ | * | # | |
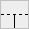 | 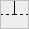 | 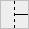 |  |  | 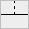 |  |  |  | 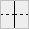 |
We'll refer to these elements as connection tiles.
Style of diagram elements
You can change border color and background color of a block. It's done by specifying block parameters in abbreviation description right before equal sign and within curly brackets. Parameters should be formatted as key:value and separated by semicolon. There are two keys supported: border-color for a color of border and background-color for a color of background. Color values should be specified in CSS2 format including SVG color keywords.
<diagram>
| AAA | | | | |F|~|~|~|7| |AAA{border-color:blue;background-color:lightgreen}=Border is blue,\\ background is lightgreen
| |!| | | | | CCC | | DDD |CCC{border-color:#a9c}=Border is #a9c,\\ background is transparent|DDD{border-color:silver;background-color:silver;}=Border is silver,\\ background is silver
| BBB | | | | | | | | | | |BBB{border-color:rgb(0%,50%,0%);background-color:#abcdef}=Border is green,\\ background is #abcdef
</diagram>
| Border is blue, background is lightgreen |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Border is #a9c, background is transparent |
Border is silver, background is silver |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Border is green, background is #abcdef |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
There is also possible to setup text alignment and internal indent using text-align and padding properties:
<diagram>
|Left| |Left{text-align:left;}=Text is\\ aligned to the left
| |!|
| |`|-|-|Center| |Center=By default text is aligned\\ to the center
| | | | | |!|
| | | | | |`|-|-|Right|Right{text-align:right;padding:1em}=Align text\\ to the right\\ and setup indents
</diagram>
| Text is aligned to the left |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| By default text is aligned to the center |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Align text to the right and setup indents |
||||||||||||||||||||||
You can note here that it's allowed to skip empty sections in the end of a row as in the last example. But you should be aware of some difficulties in futher editing of diagram and influence on block width. Besides you can change spacing between blocks by introducing more columns and rows (this works because of minimal height and width of each empty block). Compare
<diagram> | AAA |-| BBB | | |:| | | | | | | DDD | | |L|~|~| CCC | </diagram>
| AAA | BBB | |||||||||||||||||||||
| DDD | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| CCC | ||||||||||||||||||||||
with
<diagram> | AAA |-|-|-| BBB | | | | | | | | |:| | |:| | | | | | | | | | | DDD | | |:| | |L|~|~|~|~| CCC | </diagram>
| AAA | BBB | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DDD | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CCC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Arrows
You can use arrows in diagrams. For example,
<diagram> | AAA |-@2| BBB |-@a| EEE | | |:@1| | | |!@4| | | |}@72|-|-| GGG | | DDD |~@8| CCC | | FFF | </diagram>
| AAA | BBB | EEE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| GGG | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DDD | CCC | FFF | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
To insert an arrow you should put '@' and one or two symbols as direction settings after а control character. The first symbol sets arrows that are pointed out of the center of connection tile. It's a hexadecimal number that has 4 bits for each of 4 directions: Up, Right, Down, Left. Each bit sets the presence of an arrow in the corresponding direction. If you're not familiar with hexadecimal representation then use the following algorithm. Calculate a sum of direction numbers using this table:




